Book Now
Services
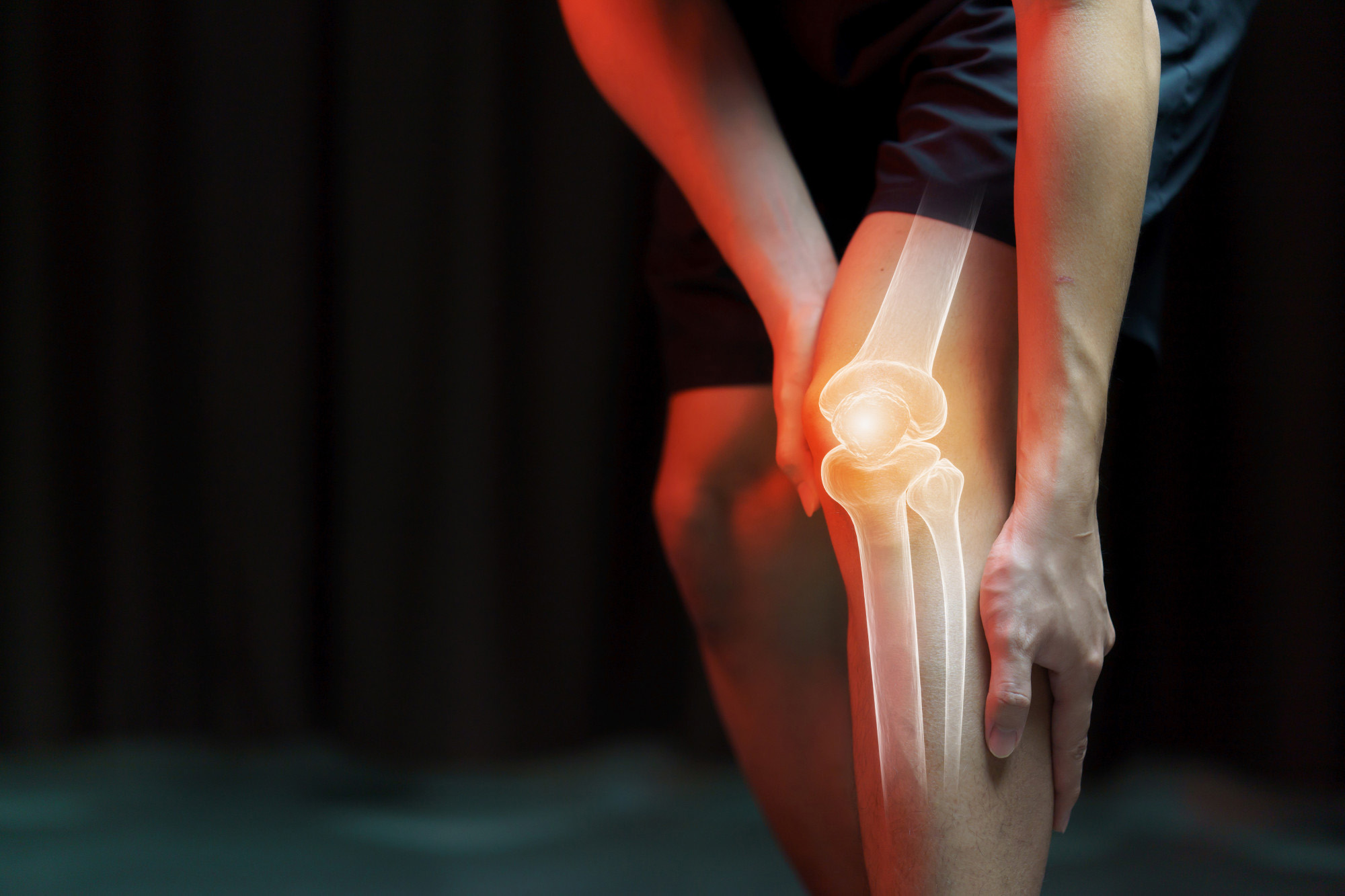
Knee Pain
Knee pain is a common problem that can originate in any of the bony structures compromising the knee joint (femur, tibia, fibula), the kneecap (patella), or the ligaments and cartilage (meniscus) of the knee. Knee pain can be aggravated by exercise, affected by the surrounding muscles and their movements, and be triggered by other problems (such as a foot injury). Knee pain can affect people of all ages, and home remedies can be helpful unless it becomes severe.
Symptoms
The location of the knee pain can vary depending on which structure is involved. With infection or an inflammatory process, the whole knee might be swollen and painful, while a torn meniscus or fracture of a bone gives symptoms only in one specific location. A Baker cyst will usually cause pain in the back of the knee. The severity of the joint pain can vary, from a minor ache to a severe and disabling pain. Some of the other signs and symptoms that accompany knee pain are:
Difficulty walking due to instability of the knee,
Limping due to discomfort,
Difficulty walking up or down steps due to ligament damage,
Locking of the knee (unable to bend the knee),
Redness and swelling,
Inability to extend the knee, and
Shifting weight to the opposite knee and foot.

Causes
Knee pain can be divided into three major categories:
Acute injury: such as a broken bone, torn ligament, or meniscal tear
Medical conditions: arthritis, infections
Chronic use/overuse conditions: osteoarthritis, patellar syndromes, tendinitis, and bursitis
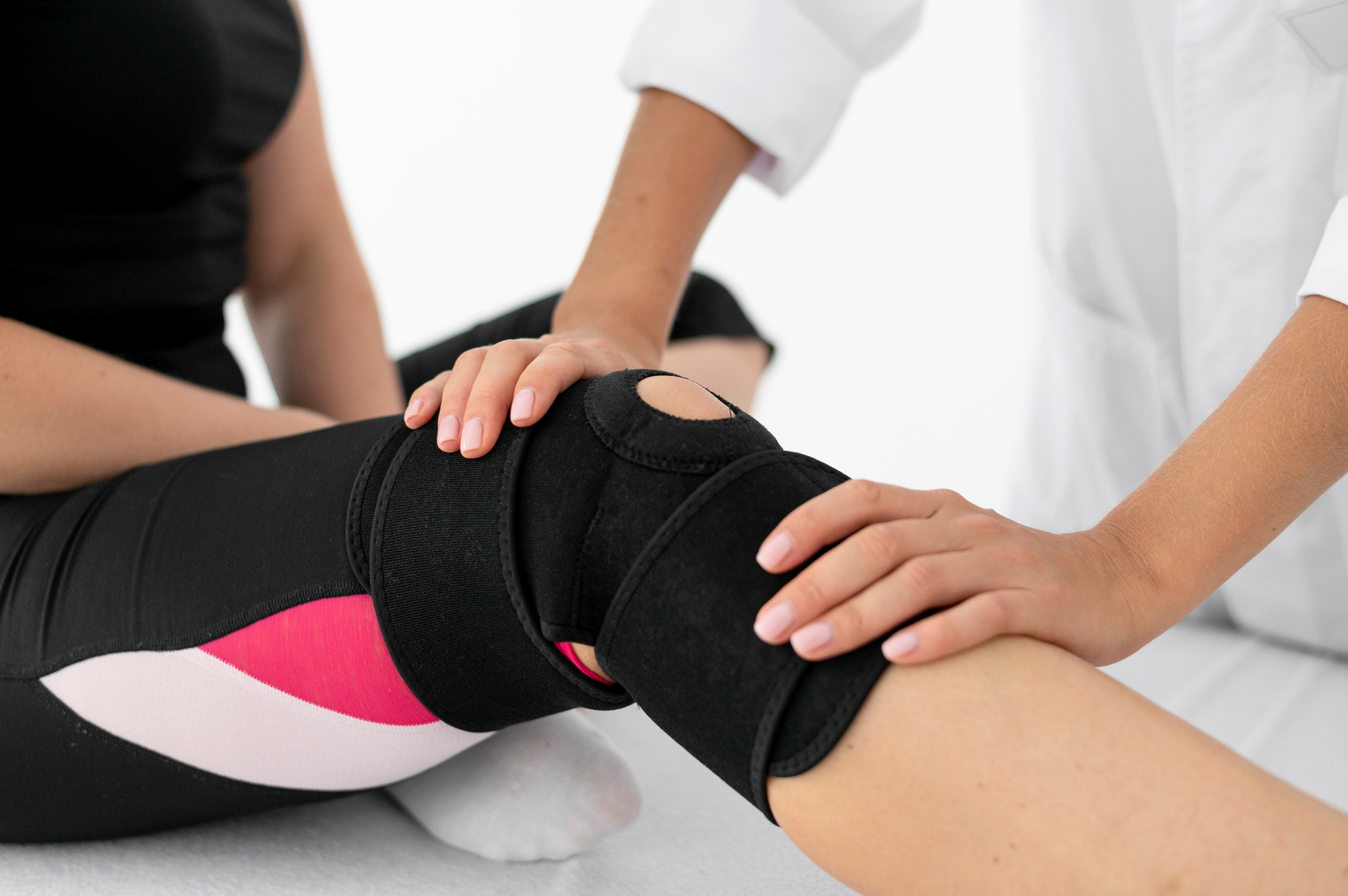
Treatment
Treatments for knee pain are as varied as the conditions that can cause the pain.
Medications - Medications might be prescribed to treat an underlying medical condition or for pain relief. If you are taking over-the-counter pain medications regularly for your knee pain, you should see your doctor to be evaluated.
Physical therapy - Sometimes strengthening the muscles around the knee will make it more stable and help guarantee the best mechanical movements. This can help avoid injuries or further worsening of an injury.
Injections - Injecting medications directly into your knee might help in certain situations. The two most common injections are corticosteroids and lubricants. Corticosteroid injections can help arthritis and other inflammations of the knee. They usually need to be repeated every few months. Lubricants that are similar to the fluid already in your knee joint can help with movement and pain.
Surgery - Knee operations range from arthroscopic knee surgery to total knee replacement. Arthroscopic knee surgery is a very common surgical procedure that allows the physician look inside your knee through a few small holes and a fiberoptic camera. The surgeon can repair many of the injuries and remove small pieces of loose bones or cartilage. This is a common outpatient procedure.
Partial knee replacement - The surgeon replaces the damaged portions of the knee with plastic and metal parts. Because only part of the knee joint is replaced, this procedure has a shorter recovery then a total knee replacement.
Total knee replacement - In this procedure, the knee is replaced with an artificial joint.

