MRI Scan
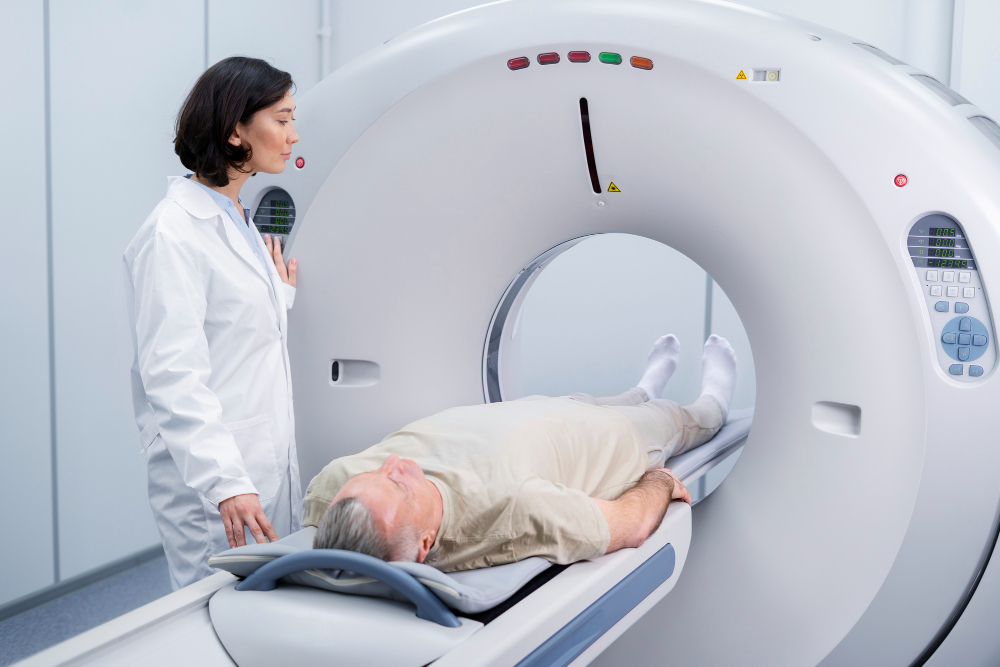
MRI or Magnetic Resonance Imaging is a type of imaging technology that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the organs and tissues within the body.
As such, they're widely used in medicine to diagnose a variety of medical conditions and guide treatment plans. For instance, they can help detect tumors, damage from a heart attack, brain injuries, spinal cord injuries, stroke, and much more.
Uses
Below mentioned are some common uses of MRI scans.
- Brain & Spinal Cord: An abnormality of the brain or spinal cord is frequently diagnosed via an MRI scan.
- Bones & Joints: MRIs can reveal detailed images of bone and joint abnormalities such as arthritis, bone infections, fractures that may not be visible on X-rays, and injuries to tendons and ligaments.
- Heart & Blood Vessels: Cardiac MRI can provide information about the structure and function of the heart. It's used to assess damage from heart disease.
- Breasts: It can also be used to better evaluate abnormalities detected on a mammogram.
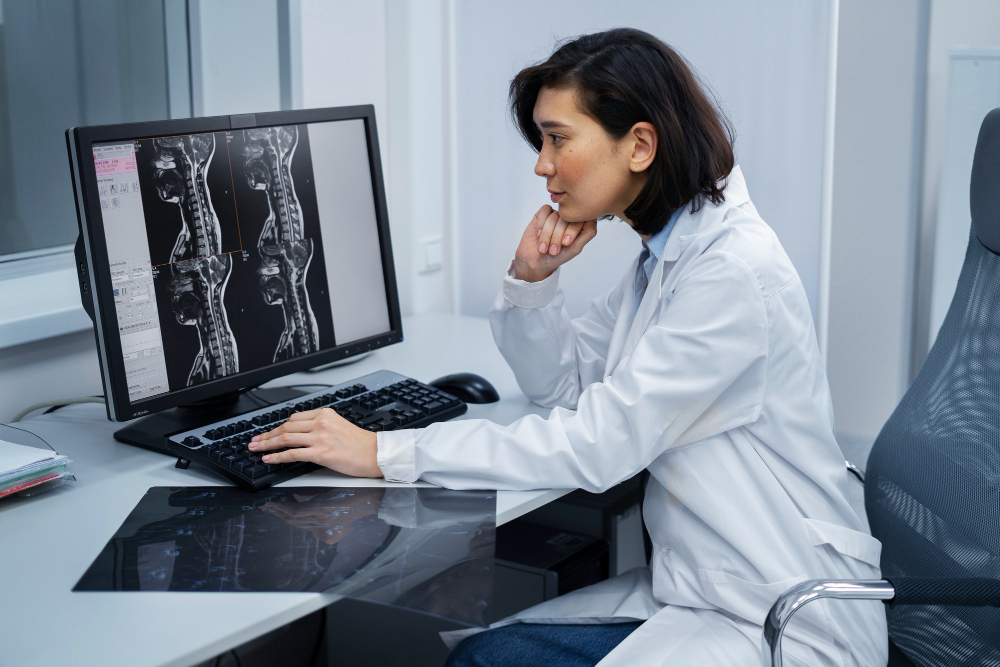
- Other Organs: Other organs in the body can be seen and evaluated using an MRI scan, which is frequently helpful in the detection and management of diseases like cancer.
- Functional MRI (fMRI): This is a specialized MRI technique that monitors metabolic alterations in the brain to better comprehend how it functions.
- Vascular Imaging: MRIs can be used to visualize blood vessels and blood flow, helping to detect blockages or aneurysms.
- MRIs with Contrast: Sometimes, a contrast agent is used to make certain tissues or abnormalities more visible. The contrast agent is injected into a vein before or during the MRI.
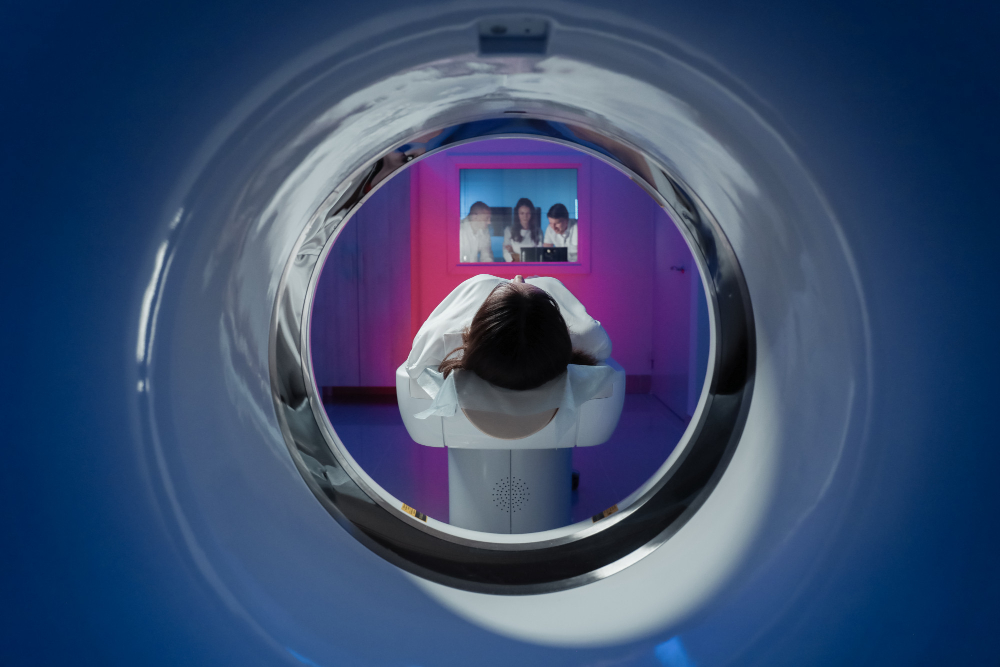

Here's a general outline of what you can expect during an MRI procedure:
- Preparation: You'll be asked to remove all jewelry, clothing containing metal (zippers, hooks, etc.), hearing aids, glasses, and any removable dental work.
- Screening: Prior to the scan, you'll be asked about anything that might create a health risk or interfere with imaging.
- Positioning: You will lie down on a movable examination table. Doctors will use straps and bolsters to help you stay still and maintain the correct position during the procedure.
- Scanning: The examination table will then be moved into the magnet of the MRI unit, and the radiologist and technologist will leave the room while the MRI examination is performed.
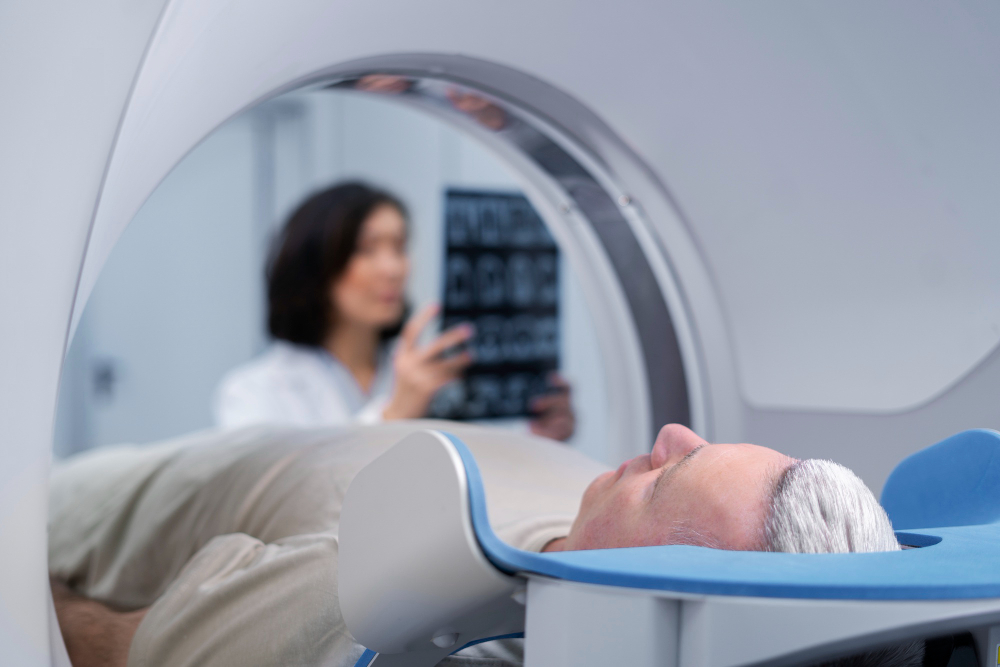
Like any medical procedure, it does have some potential risks, which include:
- Allergic Reactions: In some cases, a contrast agent is used to improve the clarity of the MRI images.
- Impaired Kidney Function: The contrast agent used in some MRI scans can lead to nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in people with severe kidney failure.
- Pregnancy: MRIs with contrast are usually avoided throughout the entire pregnancy.
- Claustrophobia: In the confining environment of the MRI machine, some persons may experience discomfort or claustrophobia.
- Noise: MRI machines can be quite loud, which might be uncomfortable for some patients.
- Heating: There's a small risk that the radiofrequency energy used by the MRI machine can lead to a rise in body temperature.

A common diagnostic imaging method that does not require an incision that allows doctors to see inside the body is X-ray imaging. They can use this to recognize, monitor, and treat a range of medical conditions.
X-rays provide images of the inside of the body using electromagnetic radiation. various tissues absorb the X-rays in various amounts as they travel through the body.
For example, bones, which are dense tissues, will block most of the radiation and appear white on an X-ray image, while softer tissues, like muscles or organs, will appear in shades of grey because they let more radiation pass through.
Below mentioned is a general outline of what you can expect during an X-ray.
- Preparation: Any jewelry, eyeglasses, or metal objects that can obstruct the X-ray images will need to be taken off.
- Positioning: You'll be positioned on an X-ray table or asked to stand against a specialized plate that captures the X-ray images.
- Protective Shielding: If certain parts of your body aren't being imaged, they might be covered with a lead apron or other protective shield to minimize exposure to radiation.
- X-Ray Imaging: The X-ray machine will be positioned over the area of your body to be examined.
Like any medical procedure, it does have some potential risks, which are mentioned below.
- Radiation Exposure: Ionizing radiation does have the ability to harm cells, which over time may raise the chance of developing cancer.
- Allergic Reactions to Contrast Media: In some cases, a contrast agent may be used to make certain tissues or structures more visible.
- Pregnancy: An unborn kid may suffer injury from X-rays, especially in the early stages of pregnancy.
- Radiation Risks in Children: Children are more susceptible to the consequences of radiation exposure than adults are, and they should experience these effects for a longer projected lifetime.
- Contrast-Induced Nephropathy: In people with impaired kidney function, the contrast agent used in some types of X-ray imaging can, in rare cases, lead to further kidney damage.

