Book Now
Services
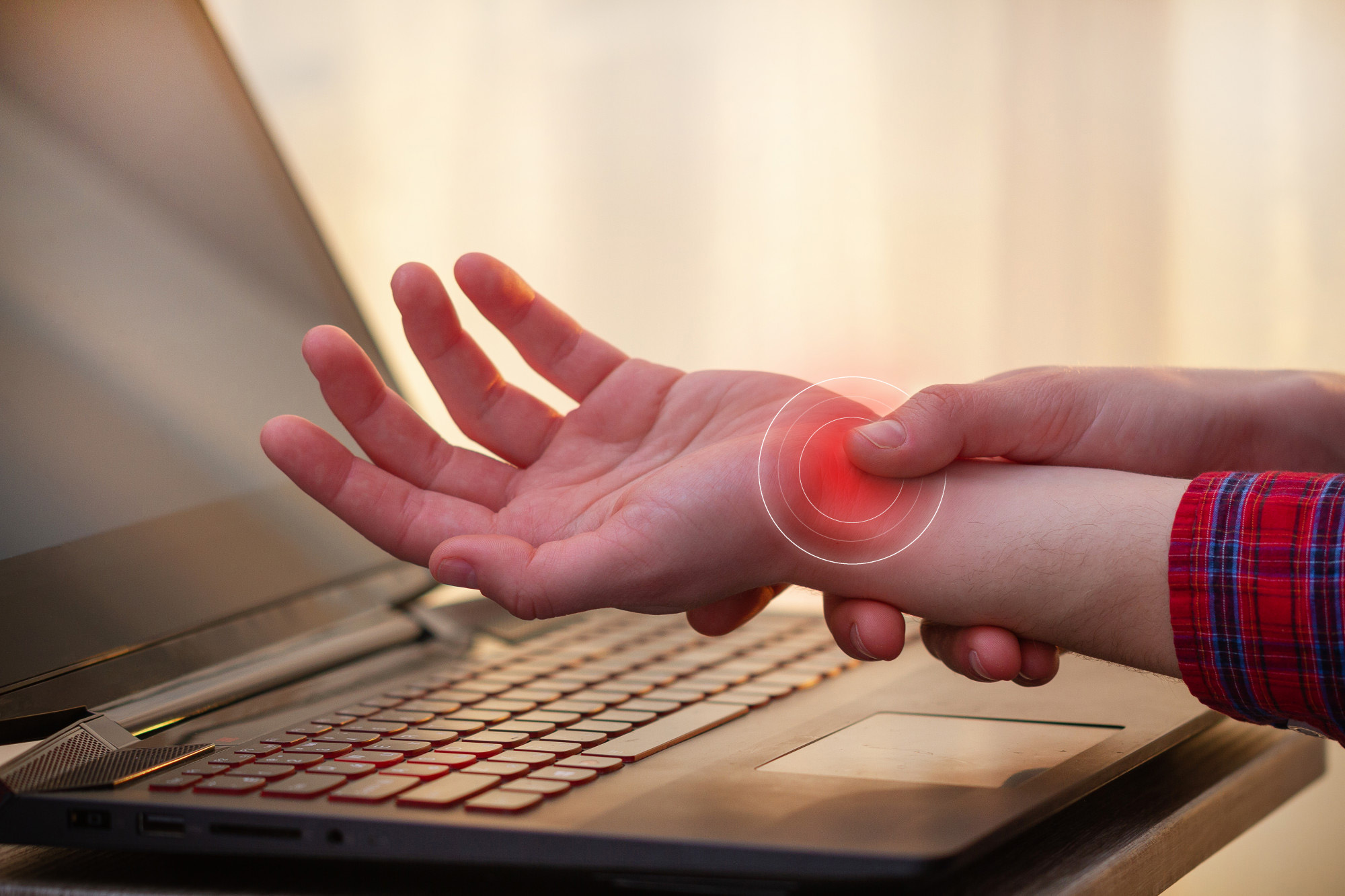

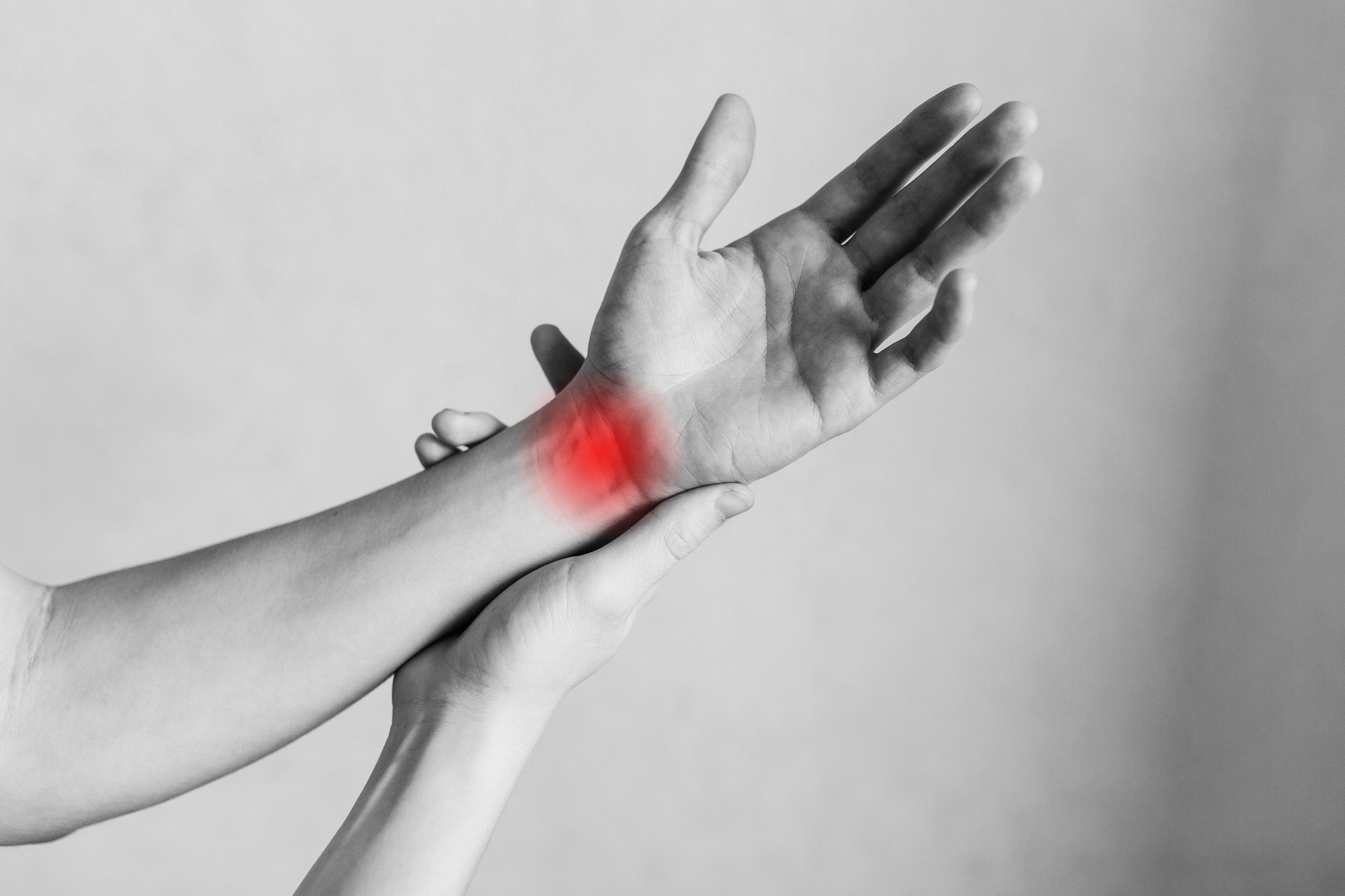
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition caused by a pinched nerve in the wrist, causing numbness, weakness, and pain in the hand.
Symptoms
Compression of the median nerve causes tingling, numbness, weakness of the hand, which we call carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Tingling or numbness – in the thumb, index, middle and ring fingers, except the little finger. This sensation may radiate from the wrist to the arm.
- Weakness – dropping objects may be because of the weakness of the pinching muscles of the thumb, or numbness felt from the fingers, wrist, and/or the arms
- Electric shock-like feeling in the fingers and thumb
- Pain in the hand and fingers
Causes
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when the median nerve is compressed, due to the swelling of the synovium. Although in most cases, there is no specific cause of carpal tunnel syndrome, we do have these contributing factors:
- Heredity/Race – carpal tunnels are smaller in some people, and this is usually hereditary.
- Anatomic factors – aside from heredity, the carpal tunnel space may become smaller in cases of wrist fracture, dislocation, or arthritis exerting pressure on the median nerve.
- Chronic conditions such as diabetes, wherein there is increased risk for nerve damage, including the median nerve.
- Medical conditions such thyroid problems and kidney disorders.
- More common in women than in men, probably because the carpal tunnel is relatively smaller in women.
- More common in older people, with a peak age range of 45-60 years.
- Hand use and workplace factors – prolonged or repetitive flexing of the wrist (keyboarding and excessive mouse use), or working with vibrating tools may damage the median nerve.

Treatment
With early diagnosis, these conservative managements would be very useful in slowing or stopping the progression of the disease.
- If the condition is caused by an occupation or specific activity, this has to be modified (e.g., use of wrist rest when using the keyboard), moderated or even stopped, to prevent worsening of the symptoms
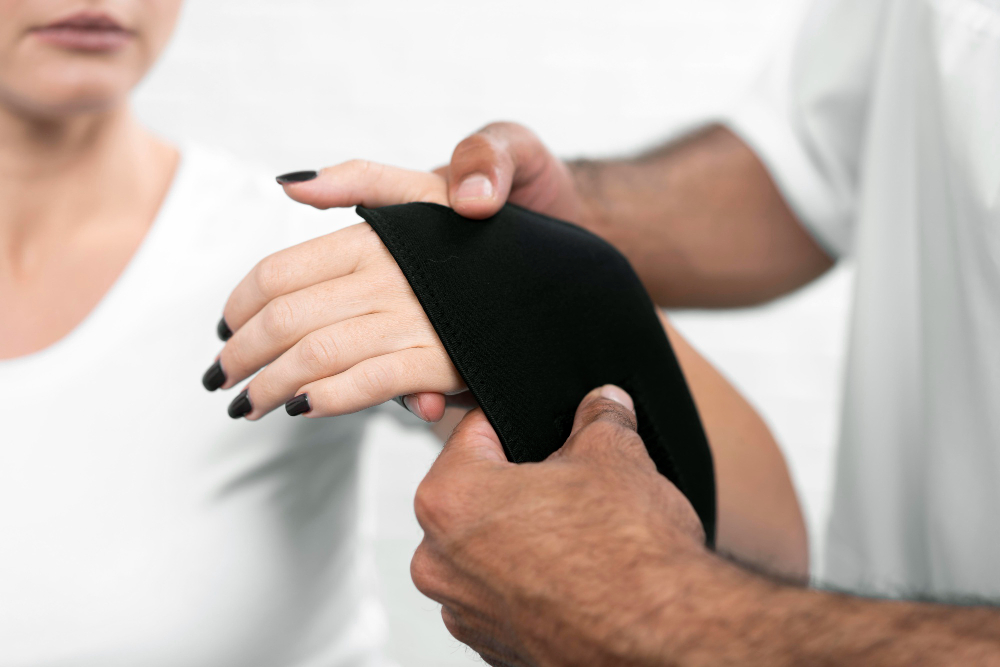
- Splints - in some cases, wearing a wrist splint can help. Splinting may prevent certain wrist movements that cause irritation. A splint might also reduce squeezing of the nerve.
- Bracing or splinting – to keep the wrist from bending, especially during sleeping or other activities where symptoms grow worse.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are helpful in relieving pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroid injection – decreases swelling and inflammation, relieving pressure on the median nerve, therefore relieving the symptoms.

Prevention
- If you exercise, stay at a healthy weight, control other health conditions such as arthritis and diabetes, and avoid smoking, you can help prevent carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Proper body mechanics are key to preventing carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Evaluate your daily routine for activities that increase your risk of carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Take frequent breaks from activities to rest, stretch, change positions, or alternate with another activity.

