Book Now
Services

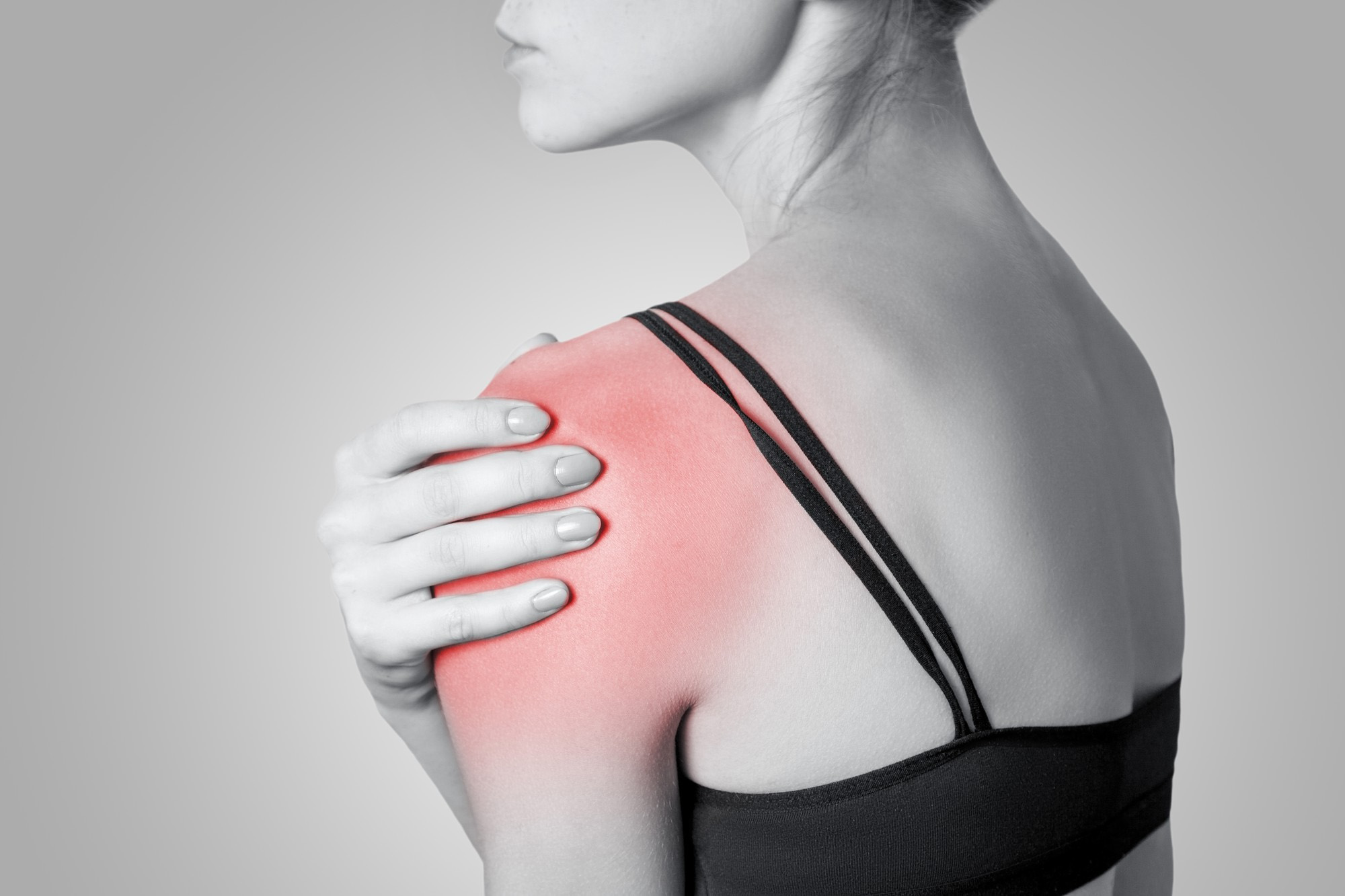
Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy
A fracture is a condition in which there is a break in the continuity of the bone. This happens almost instantly as a result of an impact, stress, or other type of trauma to the bone. This may also be a result of certain conditions such as osteoporosis or bone cancer.
Symptoms
The pain that one may be feeling around their shoulder could be related to:
Tendinitis – meaning inflammation of the tendon – with its “great responsibility” it is more prone to get irritated and then may cause inflammation.
Bursitis – meaning inflammation of the bursa – the lubricating sac found in between the bones and the rotator cuff. Irritation and inflammation can occur in this area as well.
Impingement – as you do overhead raises, the rotator cuff is pushed upward towards the bones. When done repeatedly, inflammation can occur in the tendon and/or bursa.
Calcific – as a result of the body trying to heal, calcium deposits may accumulate in the injured part of the tendon.
Causes
Athletes, cabin crews, and those who rely on repetitive overhead raises to do their job, are prone to developing this condition. It may also be a direct result of injury or trauma to the shoulders. Additionally, it may develop without any apparent reason. This condition is also linked to age. The older the person, the higher the chance of developing this condition. Lifestyle also plays a big role, as most people who develop this condition are habitual smokers.
Treatment
To address your chief complaints, you and our specialists can decide as to which treatment is appropriate for your condition. Some of the choices would be as follows:
Rest – avoid or limit overhead activities.
Anti-inflammatories – to lessen the inflammation.
Physiotherapy – for restoration of normal motion, stretching, and strengthening.
Steroid injections – if conservative management is not enough to manage your symptoms, this can be an option.
Ultrasound-guided needling and aspiration– applicable for calcific tendinopathy. Your specialist can do this procedure using only local anesthesia. You then will be evaluated with x-rays to determine your progress following the procedure.
Surgery – should all else fails or if the tendinopathy is very severe that no conservative
management could be done to alleviate the symptoms, surgery can be done.
Prevention
Keep the muscles in your shoulders flexible and strong. Daily exercises to maintain strength and flexibility may be the best defence against rotator cuff disorders. Have good posture at all times. Stand straight and relaxed, without slumping. To strengthen your rotator cuff, it's best to use lower resistance with more repetitions. Low resistance exercises gradually strengthen these small muscles without the risk of injury.

